Author details
Author's Published Works
K. Yoshino;T. Takeshita;I. Kotaka;S. Kondo;Y. Noguchi;R. Iga;K. Wakita
K. Sato;I. Kotaka;A. Hirano;M. Asobe;Y. Miyamoto;N. Shimizu;K. Hagimoto
K. Wahita;K. Yoshino;S. Matsumoto;I. Kotaka;N. Yoshimoto;S. Kondo;Y. Noguchi
F. Zamkotsian;K. Sato;H. Okamoto;K. Kishi;I. Kotaka;M. Yamamoto;Y. Kondo;H. Yasaka;Y. Yoshikuni;K. Oe
K. Yoshino;K. Wakita;I. Kotaka;S. Kondo;Y. Noguchi;S. Kuwano;N. Takachio;T. Otsuji;Y. Imai;T. Enoki
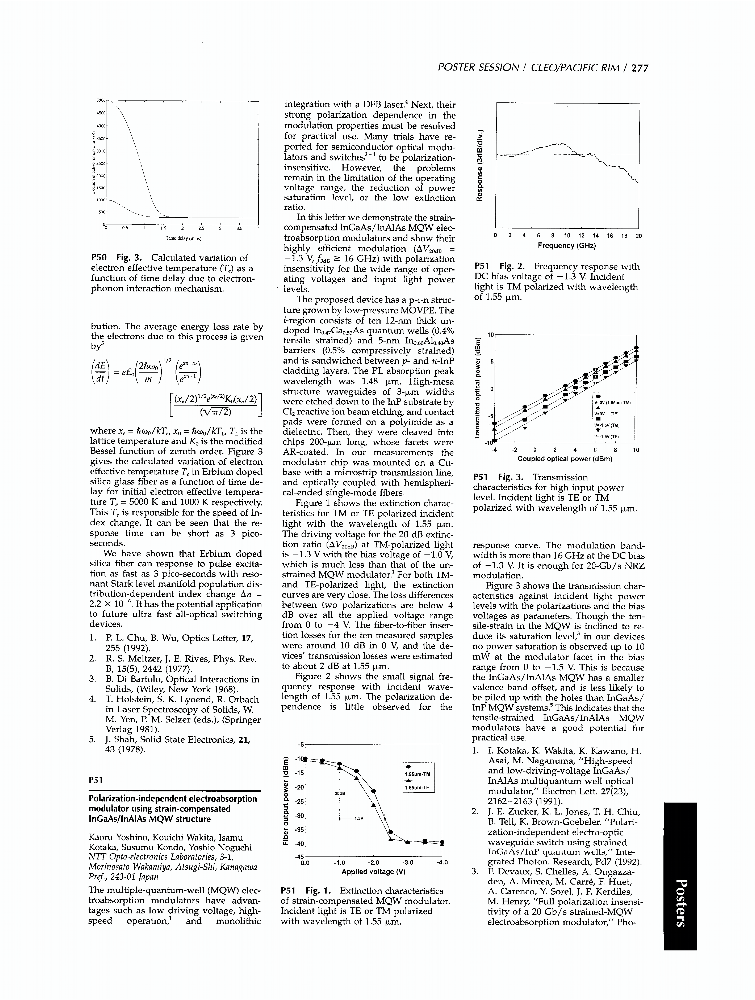 Show More
Show MoreM. Wada;M. Kohtoku;K. Kawano;S. Kondo;Y. Tohmori;Y. Kondo;K. Kishi;Y. Sakai;I. Kotaka;Y. Noguchi;Y. Itaya
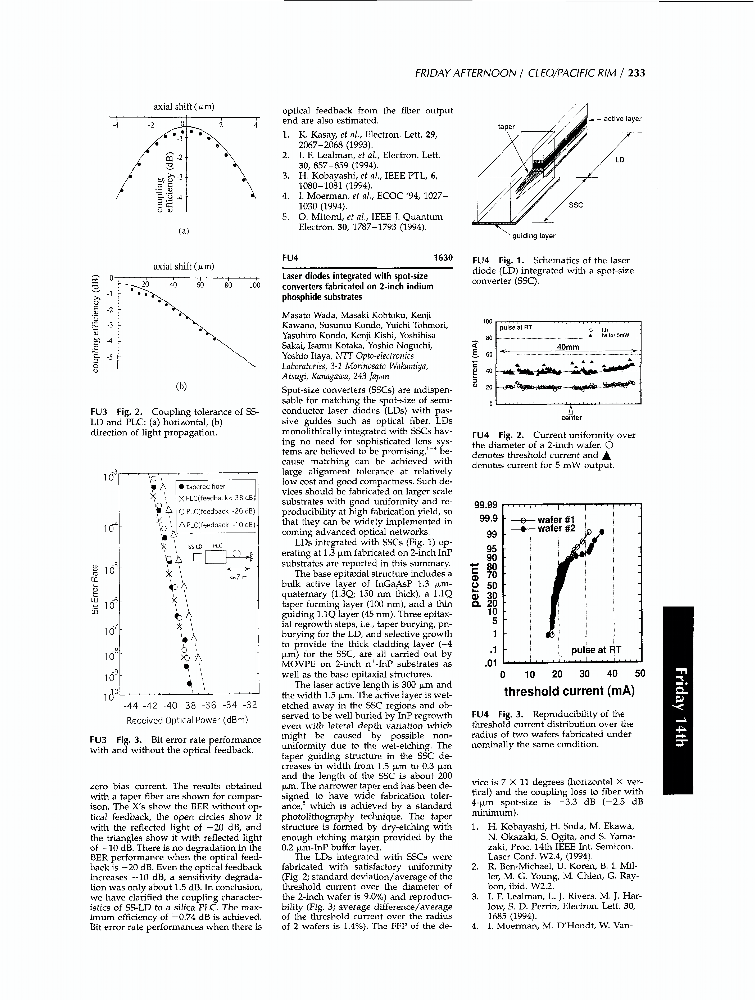 Show More
Show MoreO. Mitomi;S. Nojima;I. Kotaka;K. Wakita;K. Kawano;M. Naganuma
K. Wakita;I. Kotaka;O. Mitomi;H. Asai;Y. Kawamura;M. Naganuma
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity.
© Copyright 2025 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.