Introduction
An efficient mobility system, both in terms of the offered transport services and from an energy perspective, is one of the essential requirements of smart cities [1]. In particular, the transition to smart mobility could take place in several ways, either through the adoption of green technologies, such as electric vehicles, or through the use of vehicles with a high level of automation that can provide both better performance and higher levels of safety. However, merely moving towards technologically advanced means of transport is not sufficient to turn cities into less polluted and more accessible places. Therefore, it is necessary to change the mobility habits of citizens, encouraging them to prefer collective transport systems over private vehicles. On the other hand, public transport services should be reconsidered both with the aim of adapting to these new technologies and to be more flexible and better suited to current mobility needs.
The planning and control issues widely studied for fossil fuel buses (see the survey paper [2]) need to be revised to consider the charging requirements [3] and the automated or semi-automated features of these vehicles [4], [5]. Thus, strategic, tactical, and operational planning and control problems must be reformulated in this new scenario. In particular, decisions made at the strategic level should also concern the choice of equipment installed on vehicles and charging infrastructure [6], the location of charging stations [7], and the sizing of the bus fleet. Some of these decisions can be made jointly. For example, [8] and [9] define the type of on-board technologies and the location of charging points at the same time, while in [10] a planning problem is proposed to determine the optimal number of electric buses in the fleet based on the technological equipment of the vehicle and the charging infrastructure. At the tactical level, decisions are mainly related to the definition of frequency and timetable with the goal of considering the energy needs of electric buses [11]. At the operational level the problems of vehicle scheduling and dispatching are particularly crucial since they are related to the availability of the charging infrastructure. Works addressing these issues are for example [12], [13], [14], [15]. Furthermore, when considering electric vehicles, the influence of the surrounding traffic becomes particularly relevant on the effective energy consumption and thus on the actual ability to complete the tasks assigned to each vehicle, as, for instance, illustrated in [16] where an electric bus schedule in presence of stochastic traffic conditions is proposed.
As far as control approaches are concerned, most of those present in the literature are targeted at the control of fossil-fuel buses. However, regardless of the bus type, the main control approaches can be distinguished into station control strategies, in which the control actions are implemented at bus stops and which typically involve the decision regarding the dwell time at stops [17], [18], and inter-station control strategies that are taken while the bus is traveling between two stops and are generally based on the control of the bus speed [19], [20]. Note that most of the approaches related to the control of electric buses fall into the category of inter-station control, combining the concepts already developed in eco-driving strategies for electric vehicles with the need to ensure efficient public transport services. An example of an eco-driving approach applied to the control of electric buses is presented in [21], [22]. Moreover, some works integrate station control with inter-station control, resulting in combined approaches that involve the implementation of multiple control actions at the same time. For instance, [23] and [24] combine the typical purposes of eco-driving control with the goal of limiting bus bunching.
This work falls in this line of research by integrating station and inter-station control through a Pareto-optimal event-based control scheme allowing to find the optimal bus speed during the trip and the dwell/charging times at bus stops. This optimal solution is obtained by solving, in real time, a multi-objective optimal control problem formalized to minimize deviations from the timetable and to achieve a final energy level that allows the bus to perform a subsequent ride. The main peculiarity of this approach lies in the fact that the bus performs the transport service on an intercity line, where the absence of reserved lanes requires that the control actions applied to the bus are defined according to traffic predictions on the bus route. Note that the approaches already present in the literature generally do not consider the influence of vehicular traffic on the bus control scheme. Whenever reserved lanes are not present both in urban and in intercity lines, this assumption can no longer be applied since the capability of each bus to perform the transport tasks is significantly affected by the traffic conditions it encounters along its route. Notice that our previous works [25], [26], [27], [28] also relate to this line of research. Yet, differently from what addressed in them, the goal of this paper is to propose a control algorithm in which at each stop a multi-objective optimal control problem is solved by applying a specific Pareto-optimal solution. The choice of the solutions to be applied in real time is given by the occurrence of some events originating from the simultaneous verification of conditions derived from the system state detected in real time and the traffic conditions predicted over the bus line.
To summarize, the new contributions of this work are as follows:
this work proposes two methods based on the lexicographic approach combined with the epsilon-constrained method to determine the Pareto optimal solutions of sixteen scenarios characterized by different traffic conditions, values of initial energy stored in the bus battery and initial travel delay. This analysis has revealed interesting properties of the system under study that have been used to develop the control scheme to be applied in real time;
a novel Pareto-optimal event-based control scheme is proposed to properly control the speed, dwell time and charging time of an automated and electric bus. This control scheme is of decentralized type and, depending on the occurrence of a certain event, allows to decide which lexicographic control problem to solve. The events, each of which corresponds to the solution of a specific optimal control problem, have been derived from the observations made on the determination of the Pareto optimal solutions in numerous scenarios;
the proposed control scheme has been applied to a case study, demonstrating its effectiveness compared to other state-of-the-art methods and showing its practical applicability due to the limited computational time required to solve each optimal control problem. Such limited computational effort suggests the possible extension of the proposed control scheme to the centralized case in which buses belonging to a fleet are simultaneously controlled;
compared to our previous works, the multi-objective optimization problem proposed here presents some modifications, such as the introduction of a constraint on the maximum bus charging time at the terminus.
This paper is structured as follows. Section II provides the main information about the basic settings of the considered problem and of the traffic prediction model. Section III introduces the multi-objective optimal control, whose Pareto front analysis is performed on different real case study scenarios in Section IV. Note that the analysis proposed in Section IV is preliminary to the definition of the control algorithm presented in Section V. The aim of this latter is to choose which Pareto-optimal solutions to actuate in real time based on some state and scenario conditions. Section V also presents the results obtained from the application of the proposed event-based control algorithm to a real case study and compares them with those obtained from the application of state-of-the-art methods. Finally, in Section VI, final remarks and conclusions of this work are presented.
Intercity Bus Line Modeling: Notation, Basic Settings and Traffic Prediction
This section provides information on the settings of the intercity bus line considered in this paper, and the basic requirements of traffic predictions tools to be used in the optimal control problem described in Section III. Furthermore, Table 1 provides an overview of the notation adopted in this work.
The intercity line has several stops, we denote with
$\pi _{s}$ $s$ $\Pi _{s}$ $s$ $s-1$ $\eta _{s} \in \lbrace 0,1\rbrace$ $s$ $\varsigma$
Moreover, each bus in this line is associated with a timetable indicating the dwell times at each stop. The time horizon over which the bus is controlled is based on that timetable and starts at the bus departure time from stop
$\bar{w}_{s}(k) \in \lbrace 0,1\rbrace$ $k \in \mathcal {K}$ $\forall k=k^\mathrm{a}_{s}, \ldots, k^\mathrm{d}_{s}$ $k^\mathrm{a}_{s}$ $s$ $k^\mathrm{d}_{s}$ $s$ $T^\mathrm{w}_{s}$ $s$ $T^\mathrm{t}_{s}$ $s-1$ $s$ $\bar{v}_{s}$ $s-1$ $s$
A peculiar aspect of this problem is that, due to the lack of reserved lanes, the journey of the bus is affected by the surrounding traffic conditions, particularly by the speed of vehicular traffic it encounters along its route. Therefore, predictions of average traffic speed along the line should be taken into account when controlling bus speed. Such traffic predictions can be provided either by dynamic traffic models (see the survey paper [29] and the references therein) or by data-driven models (see for instance [30]). Usually these models are discretized both in space and time. The space discretization in dynamic traffic models is often associated with the road topology, whereas, when data-driven models are adopted, the number of sections is given by the number of available sensors able to provide traffic measurements. It is worth noting that the discretization used in the traffic prediction models can be different from the one used in the optimal control problem, so the traffic speed provided by the prediction models must be processed appropriately for being used in the control scheme.
In this problem we assume that the traffic prediction is performed on
the Multi-Objective Optimization Problem
In this section we introduce the multi-objective optimization problem that will be embedded into the event-based control scheme described in Section V.
Let us start by introducing the main variables adopted in this problem and, in particular, by defining the state variables used to describe the dynamics of the bus. They are the position of the bus
The control variables are the speed of the bus ![]() \begin{align*}
w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if bus is waiting at}\ s\ \text{at time}\ k\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{1}\\
c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if bus is charging at}\ s\ \text{at time}\ k\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{2}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if bus is waiting at}\ s\ \text{at time}\ k\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{1}\\
c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if bus is charging at}\ s\ \text{at time}\ k\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{2}
\end{align*}
$z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)$ $i$ $k$ \begin{equation*} z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \geq p_{i}\\ 0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{3} \end{equation*} View Source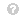 \begin{equation*}
z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \geq p_{i}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{3}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \geq p_{i}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{3}
\end{equation*}
$y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)$ $i+1$ $k$ \begin{equation*} y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \leq p_{i+1}\\ 0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{4} \end{equation*} View Source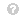 \begin{equation*}
y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \leq p_{i+1}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{4}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \leq p_{i+1}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{4}
\end{equation*}
$\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)$ $i$ $k$ \begin{equation*} \lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=1\\ 0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{5} \end{equation*} View Source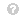 \begin{equation*}
\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=1\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{5}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)=1\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{5}
\end{equation*}
A second type of auxiliary variables concerns bus arrivals and departures at stops. These variables are defined for each stop
$\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)$ $s$ $k$ $k+1$ \begin{equation*} \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; \text{ {bus} arrives at s} \\ & \text{between k and k+1}\\ 0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{6} \end{equation*} View Source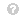 \begin{equation*}
\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; \text{ {bus} arrives at s} \\
& \text{between k and k+1}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{6}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; \text{ {bus} arrives at s} \\
& \text{between k and k+1}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{6}
\end{equation*}
$\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k)$ $s$ $k$ $k+1$ \begin{equation*} \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; \text{ {bus} departs from s} \\ & \text{between k and k+1}\\ 0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{7} \end{equation*} View Source \begin{equation*}
\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; \text{ {bus} departs from s} \\
& \text{between k and k+1}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{7}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k)=\left\lbrace \begin{array}{ll}1 & \text {if} \; \text{ {bus} departs from s} \\
& \text{between k and k+1}\\
0 & \text {otherwise} \end{array} \right. \tag{7}
\end{equation*}
Finally, another auxiliary variable is needed to represent the negative difference between the level of energy stored in the bus battery and the desired energy level ![]() \begin{equation*}
\zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}}=\max \lbrace \bar{e}^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} - e^\mathrm{{bus}}(K), 0\rbrace \tag{8}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
\zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}}=\max \lbrace \bar{e}^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} - e^\mathrm{{bus}}(K), 0\rbrace \tag{8}
\end{equation*}
A. State Equations of the Bus
The bus dynamics is given by two state equations, regarding the position of the bus and the state of the energy stored in its battery, respectively, which are included in the optimization problem as constraints, i.e.
![]() \begin{align*}
&p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1) = p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) + v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \Delta _\mathrm{T} \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{9}\\
&e^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1) = e^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)+ \Delta _\mathrm{T} \sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} \varsigma c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) + \\
&\quad - \delta \left[p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1)- p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)\right] - \Delta _\mathrm{T} \beta \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{10}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1) = p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) + v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \Delta _\mathrm{T} \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{9}\\
&e^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1) = e^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)+ \Delta _\mathrm{T} \sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} \varsigma c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) + \\
&\quad - \delta \left[p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1)- p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)\right] - \Delta _\mathrm{T} \beta \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{10}
\end{align*}
B. Constraints At Bus Stops
Some constraints are needed to correctly represent the arrival, departure, stopping of the bus at bus stops, and to enforce that the minimum service level requirements demanded for the public transport service are respected.
Let us start with constraints which impose that the bus has to stop only in the proximity of bus stops
![]() \begin{align*}
p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) - \left(\pi _{s} -\Delta \right) \geq \sigma - \left(L +\sigma \right)\left(1- w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\right) \\
s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{11}\\
\left(\pi _{s} + \Delta \right) - p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \geq \sigma - \left(L +\sigma \right)\left(1- w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\right) \\
s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{12}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) - \left(\pi _{s} -\Delta \right) \geq \sigma - \left(L +\sigma \right)\left(1- w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\right) \\
s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{11}\\
\left(\pi _{s} + \Delta \right) - p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \geq \sigma - \left(L +\sigma \right)\left(1- w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\right) \\
s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{12}
\end{align*}
Other constraints are needed to ensure that the bus cannot arrive at and depart from the same stop more than once
![]() \begin{align*}
&\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)- \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k) = w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k+1) - w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \\
&\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\qquad\qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K}\setminus \lbrace K-1\rbrace \tag{13}\\
&\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)+ \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k) \leq 1\qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{14}\\
&\sum _{ k\in \mathcal {K}}\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)+ \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k) \leq 2\qquad s \in \mathcal {S} \tag{15}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)- \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k) = w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k+1) - w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \\
&\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\qquad\qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K}\setminus \lbrace K-1\rbrace \tag{13}\\
&\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)+ \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k) \leq 1\qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{14}\\
&\sum _{ k\in \mathcal {K}}\gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{arr}}_{s}(k)+ \gamma ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{dep}}_{s}(k) \leq 2\qquad s \in \mathcal {S} \tag{15}
\end{align*}
Finally, the following constraints have been included to ensure the proper public transport service
![]() \begin{align*}
\sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \leq 1 \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{16}\\
\sum _{k \in \mathcal {K}} w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \geq \psi _{s} \qquad s \in \mathcal {S} \tag{17}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
\sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \leq 1 \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{16}\\
\sum _{k \in \mathcal {K}} w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \geq \psi _{s} \qquad s \in \mathcal {S} \tag{17}
\end{align*}
C. Constraints on Charging At Bus Stops and on the Energy Level
Some constraints are needed to model the charging phases of the bus and to impose operational requirements on the level of energy stored in the battery. The constraints related to the possibility of charging at stops are
![]() \begin{align*}
&c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \leq w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{18}\\
&c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \leq \eta _{s} \qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{19}\\
&\sum _{k \in \mathcal {K}} c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{S}(k) \leq C^{\max } \tag{20}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \leq w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{18}\\
&c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k) \leq \eta _{s} \qquad s \in \mathcal {S}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{19}\\
&\sum _{k \in \mathcal {K}} c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{S}(k) \leq C^{\max } \tag{20}
\end{align*}
Other constraints are introduced to impose some conditions on the level of energy stored in the bus battery
![]() \begin{align*}
&\zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} \geq \bar{e}^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} - e^\mathrm{{bus}}(K) \tag{21}\\
&\zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} \geq 0 \tag{22}\\
&e^\mathrm{{bus}, {\min }} \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, {\max }} \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{23}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&\zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} \geq \bar{e}^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} - e^\mathrm{{bus}}(K) \tag{21}\\
&\zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} \geq 0 \tag{22}\\
&e^\mathrm{{bus}, {\min }} \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, {\max }} \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{23}
\end{align*}
D. Constraints on Bus Speed
One of the main features of this work lies in the fact that the speed of the bus is optimized by taking into account the prediction of the average traffic speed along its route. Some constraints are then needed to compare the position of the bus with the space discretization used for traffic speed predictions. The following constraints are included to properly define the auxiliary variables introduced earlier as a function of bus position
![]() \begin{align*}
&p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) - p_{i} +M \left(1-z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\right) \geq \sigma \\
&\hphantom{}i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{24}\\
&p_{i}-p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)+M z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \geq 0 \qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \,\hphantom{} k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{25}\\
&p_{i+1}-p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)+M \left(1-y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\right)\geq 0 \\
&\hphantom{}i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{26}\\
&p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) - p_{i+1} +M y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \geq \sigma \qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K}\; \tag{27}\\
&\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \leq z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{28}\\
&\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \leq y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{29}\\
&\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \geq z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)+y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)-1\qquad\; i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K}\; \tag{30}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) - p_{i} +M \left(1-z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\right) \geq \sigma \\
&\hphantom{}i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{24}\\
&p_{i}-p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)+M z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \geq 0 \qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \,\hphantom{} k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{25}\\
&p_{i+1}-p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)+M \left(1-y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\right)\geq 0 \\
&\hphantom{}i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{26}\\
&p^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) - p_{i+1} +M y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \geq \sigma \qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K}\; \tag{27}\\
&\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \leq z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{28}\\
&\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \leq y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)\qquad i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{29}\\
&\lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) \geq z^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)+y^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k)-1\qquad\; i \in \mathcal {I}, \, k \in \mathcal {K}\; \tag{30}
\end{align*}
The following constraints are introduced to properly bound the bus speed
![]() \begin{align*}
&0 \leq v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)\leq \sum _{i \in \mathcal {I}} \lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) v^\mathrm{traffic}_{i}(k)\qquad \hphantom{}k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{31}\\
&v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \leq \bigg (1- \sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\bigg)\cdot v^\mathrm{{bus},{\max }} \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \; \tag{32}\\
&\quad -\overline{\Delta V} \leq v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1) - v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)\leq \overline{\Delta V} \\
& \hphantom{}k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{33}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&0 \leq v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)\leq \sum _{i \in \mathcal {I}} \lambda ^\mathrm{{bus}}_{i}(k) v^\mathrm{traffic}_{i}(k)\qquad \hphantom{}k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{31}\\
&v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k) \leq \bigg (1- \sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\bigg)\cdot v^\mathrm{{bus},{\max }} \qquad k \in \mathcal {K} \; \tag{32}\\
&\quad -\overline{\Delta V} \leq v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k+1) - v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)\leq \overline{\Delta V} \\
& \hphantom{}k \in \mathcal {K} \tag{33}
\end{align*}
Constraints (31) impose positivity and upper bounds for the bus speed considering the predicted speed of the traffic flow
E. Objectives and Problem Statement
The control variables of the bus are found by pursuing two different objectives named ![]() \begin{equation*}
F_{1} =\sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} \sum _{k\in \mathcal {K}}\alpha _{s}(k) \bigg (\bar{w}_{s}(k) - w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\bigg)^{2} \tag{34}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
F_{1} =\sum _{s \in \mathcal {S}} \sum _{k\in \mathcal {K}}\alpha _{s}(k) \bigg (\bar{w}_{s}(k) - w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s}(k)\bigg)^{2} \tag{34}
\end{equation*}
![]() \begin{equation*}
F_{2} = \zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} \tag{35}
\end{equation*}
\begin{equation*}
F_{2} = \zeta ^\mathrm{{bus}, \mathrm{fin}} \tag{35}
\end{equation*}
Problem 1.
Multi-objective optimal control problem: Find the state variables ![]() \begin{gather*}
\min \left(F_{1},F_{2}\right) \tag{36}\\
\text{subject to }{(9)}-{(33)}
\end{gather*}
\begin{gather*}
\min \left(F_{1},F_{2}\right) \tag{36}\\
\text{subject to }{(9)}-{(33)}
\end{gather*}
Analysis of the Pareto Front
Multi-objective optimal control problems are employed when the controller has to jointly pursue two or more objectives that may be in conflict with each other. In that case, there can be solutions in which the reduction of one objective implies an increase in the others. In multi-objective optimization, then, the different solutions may be classified according to the definition of Pareto dominance.
Referring to our specific case, let us denote by
Definition 1:
The vector
Definition 2:
A vector
Definition 3:
The Pareto front
In this section, two methods based on the integration of the epsilon-constraint method and lexicographic ordering are proposed to find the Pareto-optimal solutions of Problem 1 considering different traffic scenarios and different initial conditions related to the state of a bus, i.e. the initial amount of energy stored in bus battery and the initial delay of the ride. The choice of adopting these methods is due to the fact that Problem 1 is not convex and the application of other methods, such as the Weighted Sum Method, does not guarantee to find all points in the Pareto front (see more details on the concept of supported efficient solutions in [32] and [33]).
More in details, the Pareto-optimal solutions are sought by ranking the objectives according to a certain priority, as it is done in lexicographic approaches, and progressively reducing the bound on the non-priority objective according to the logic of the epsilon-constraint method. Since in Problem 1 there are two objectives, the possible priority orders are two and give rise to the following two methods:
Method
$\varepsilon$ $F_{1}$ $\Xi _{1}$ $\mathbf {z}^{*}_{1}$ $F_{1}$ $F_{2}$ Method
$\varepsilon$ $F_{2}$ $\Xi _{2}$ $\mathbf {z}^{*}_{2}$ $F_{2}$ $F_{1}$
In the following subsections we provide a detailed description of the two multi-objective methods and we show some results obtained by applying such methods for solving Problem 1 in a real-case study.
A. DESCRIPTION of METHODS $\varepsilon$ $F_{1}$ $\varepsilon$ $F_{2}$
Let us start by describing the first method, i.e. Method
Problem 2:
Find the state variables ![]() \begin{gather*}
\min \; F_{1} \tag{37}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{2}\leq \varepsilon _{F_{2}} \tag{38}
\end{gather*}
\begin{gather*}
\min \; F_{1} \tag{37}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{2}\leq \varepsilon _{F_{2}} \tag{38}
\end{gather*}
Problem 3:
Find the state variables ![]() \begin{gather*}
\min \; F_{2} \tag{39}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{1}= \bar{F_{1}} \tag{40}
\end{gather*}
\begin{gather*}
\min \; F_{2} \tag{39}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{1}= \bar{F_{1}} \tag{40}
\end{gather*}
where
Note that the first iteration of Algorithm 1, i.e. when
Problem 4:
Find the state variables ![]() \begin{gather*}
\rm lexmin\left\lbrace F_{1}, F_{2} \right\rbrace \tag{41}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)}
\end{gather*}
\begin{gather*}
\rm lexmin\left\lbrace F_{1}, F_{2} \right\rbrace \tag{41}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)}
\end{gather*}
Algorithm 1: Pseudocode for Method $\varepsilon$ $F_{1}$
Initialize
Initialize
Solve Problem 2 with
Solve Problem 3
Save the vector of optimal values
Fix
while Problem 2 and 3 are feasible
Solve Problem 3
Save the vector of optimal values
Fix
end while
Algorithm 2: Pseudocode for Method $\varepsilon$ $F_{2}$
Initialize
Initialize
Solve Problem 5 with
Solve Problem 6
Save the vector of optimal values
Fix
while Problem 5 and 6 are feasible
Solve Problem 6
Save the vector of optimal values
Fix
end while
The application of Method
Problem 5:
Find the state variables ![]() \begin{gather*}
\min \; F_{2} \tag{42}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{1}\leq \varepsilon _{F_{1}} \tag{43}
\end{gather*}
\begin{gather*}
\min \; F_{2} \tag{42}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{1}\leq \varepsilon _{F_{1}} \tag{43}
\end{gather*}
Problem 6:
Find the state variables ![]() \begin{gather*}
\min \; {F_{1}} \tag{44}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{2}= \bar{F_{2}} \tag{45}
\end{gather*}
\begin{gather*}
\min \; {F_{1}} \tag{44}\\
\text{subject to } {(9)}\!-\!{(23)} \text{ and}\\
F_{2}= \bar{F_{2}} \tag{45}
\end{gather*}
Note again that, even for this method, the first iteration of Algorithm 2 corresponds to solving the following lexicographic problem:
Problem 7:
Find the state variables ![]() \begin{gather*}
\rm lexmin\left\lbrace F_{2}, F_{1} \right\rbrace \tag{46}\\
\text{subject to }{(9)}\!-\!{(23)}
\end{gather*}
\begin{gather*}
\rm lexmin\left\lbrace F_{2}, F_{1} \right\rbrace \tag{46}\\
\text{subject to }{(9)}\!-\!{(23)}
\end{gather*}
It is possible to make an important remark regarding the described multi-objective methods.
Remark 1:
Method
It is worth noting that the values assumed by the parameters
B. Numerical Analysis
In this section, a numerical application of the methods introduced earlier is proposed to find the Pareto-optimal solutions related to a case study inspired by an intercity bus line located in Italy. The interurban bus line under investigation connects Savona to Finalborgo for a route of 27 kilometers. The line includes eight stops, five of which (including the terminus) are equipped with flash-charging infrastructure (see Table 2). In this analysis, two bus rides are considered, which, being operated at two different times of the day, are affected by different traffic conditions. The first bus route, named Ride A, departs from Savona at 7:13 a.m. and faces the commuter rush hour, while the second bus ride, named Ride B, departs at 2:35 p.m. and faces a route under free flow traffic conditions. The timetable of both rides is shown in Table 3.
Different initial conditions have been considered for each bus ride regarding the initial energy stored in the bus battery and the minutes of delay on departure from the Savona stop. The combination of these initial conditions resulted in eight scenarios for each ride, as shown in Tables 4 and 5.
For all the scenarios the time step
The two multi-objective methods presented above have been applied to these sixteen scenarios using different values of the parameters
The numerical results discussed in this section have been obtained by solving the optimization problems in Algorithm 1 and Algorithm 2 in Matlab using YALMIP [34] and adopting Gurobi 11 as solver. The main characteristics of sets
From the analysis of the results given in Tables 6 and 7, and, in particular, by looking at the last two columns showing the extreme solutions of the Pareto front, it is possible to state that the objectives
starting the ride with an initial energy level that is very low;
starting the ride with some delay;
finding unfavorable traffic conditions.
The most critical scenarios are those in which the bus starts the ride with a very low initial energy level (Scenarios A.1, A.5, B.1 and B.5). Indeed, in Scenarios A.1 (peak-hour scenario) and B.1 (uncongested scenario), where the bus has an initial energy level close to the minimum allowed, the number of points found in the Pareto front is two. In cases in which, in addition to a very low initial energy level, there is also an initial delay (Scenarios A.5 and B.5), either no feasible solutions have been found (Scenario A.5) or only one point in the Pareto front has been obtained (Scenario B.5). Other scenarios for which a limited number of Pareto-optimal solutions have been found are those corresponding to: Scenarios B.6-B.8 (scenarios without traffic congestion but with initial delay on the ride), Scenarios A.2-A.4 (scenarios with traffic congestion) and A.6-A.8 (scenarios with congestion and initial delay). This is because, under these conditions, the constraints ensuring a minimum level of energy stored in the bus battery and the constraints related to provide an adequate public transport service lead to a limited number of feasible solutions and consequently also to a limited number of points in the Pareto front. Note that, for the scenarios in which only two points have been found, the values of the objective functions are exactly those obtained by solving the lexicographic problems in which the priority is given alternately to the two objectives, namely solving Problem 4 and Problem 7, respectively.
On the other hand, in Scenarios B.2-B.4, characterized by free-flow traffic conditions, the absence of initial delay and an initial energy level that is not critical, the Pareto front is characterized by more than two points.
Overall, the results obtained from these sixteen scenarios suggest some remarks. First of all, it is important to note that there are some sets of critical conditions, given by the combination of the initial states of the bus (e.g., initial state of charge and initial delay) and traffic conditions on the line, such that Problem 1 has no feasible solutions. The definition of these critical conditions will be the subject of future works, while in this paper we focus on defining a control scheme aimed to optimize the bus performance in all the other cases.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that the traffic conditions encountered along the bus line severely affect the capability of the bus to meet the objectives, both in terms of timetable compliance and energy consumption, since the longer the time spent by the bus on the line is, the greater its energy consumption becomes.
the Pareto-Optimal Event-Based Control Scheme
Inspired by the analysis realized in Section IV, in this section we propose an event-based control scheme, whose general structure is shown in Fig. 1. This control scheme is founded on the solution of Problem 1 in which the choice of the priority order of one objective over the other is made on the basis of the occurrence of specific events. These events are given by the simultaneous occurrence of some conditions concerning the state of the bus and the traffic conditions on the bus line.
More in detail, each time the bus is at a stop, the traffic prediction model (see Section II) is run, and some state and scenario conditions are verified; these conditions concern:
the predicted traffic speed on the bus line (scenario-conditions);
the expected departure time of the bus at the stop (state-conditions);
the state of charge of the bus battery (state-conditions).
On the basis of the conditions that are verified, an event is identified and a lexicographic optimal control problem is solved, which reflects a specific decision on the priority to be assigned to the objectives and thus the Pareto-optimal solution to be applied in real time. This procedure is applied from the stop at which the ride begins, i.e.
A. Scenario and State Conditions
Let us denote with
Let us also denote with ![]() \begin{align*}
&\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{s+1}\left(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1}\right) \\
&\quad =\frac{1}{T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1}\cdot |\mathcal {I}_{s+1}|}\sum _{i\in \mathcal {I}_{s+1}}\sum _{k=\tilde{k}_{s}}^{\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1}} v_{i}^\mathrm{traffic}(k) \tag{47}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
&\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{s+1}\left(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1}\right) \\
&\quad =\frac{1}{T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1}\cdot |\mathcal {I}_{s+1}|}\sum _{i\in \mathcal {I}_{s+1}}\sum _{k=\tilde{k}_{s}}^{\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1}} v_{i}^\mathrm{traffic}(k) \tag{47}
\end{align*}
![]() \begin{align*}
\bar{e}_{s}\left(e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0)\right)=& e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0) - \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:r \leq s}\bigl [ \Pi _{s}\delta + \Delta _\mathrm{T} \left(T^\mathrm{t}_{r}+T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\right)\beta \bigr ] \\
& +\sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:r \leq s,\eta _{r}=1}E^{+}_{r} \qquad \forall s \in \mathcal {S} \tag{48}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
\bar{e}_{s}\left(e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0)\right)=& e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0) - \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:r \leq s}\bigl [ \Pi _{s}\delta + \Delta _\mathrm{T} \left(T^\mathrm{t}_{r}+T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\right)\beta \bigr ] \\
& +\sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:r \leq s,\eta _{r}=1}E^{+}_{r} \qquad \forall s \in \mathcal {S} \tag{48}
\end{align*}
![]() \begin{align*}
\bar{e}^\mathrm{fin} -\biggl [ e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0) - \sum _{s\in \mathcal {S}}\bigl [\Pi _{s}\delta +\Delta _\mathrm{T} \left(T^\mathrm{t}_{s}+T^\mathrm{w}_{s}\right)\beta \bigr ] \\
+\sum _{s\in \mathcal {S}:\eta _{s}=1}E^{+}_{s}\biggr ] = 0 \quad \tag{49}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
\bar{e}^\mathrm{fin} -\biggl [ e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0) - \sum _{s\in \mathcal {S}}\bigl [\Pi _{s}\delta +\Delta _\mathrm{T} \left(T^\mathrm{t}_{s}+T^\mathrm{w}_{s}\right)\beta \bigr ] \\
+\sum _{s\in \mathcal {S}:\eta _{s}=1}E^{+}_{s}\biggr ] = 0 \quad \tag{49}
\end{align*}
a) Scenario-conditions on the predicted traffic speed on the bus line
These scenario-conditions are dedicated to assess whether the bus may find congestion along its route. Therefore, considering that
$\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{s+1}(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1})\geq \bar{v}_{s+1}$ $s$ $s+1$ $\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{s+1}(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1})< \bar{v}_{s+1}$ $s$ $s+1$ $\bar{v}_{s+1} - \bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{s+1}(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1}) \leq \Delta _{v}$ $s$ $s+1$ $\Delta _{v}$
b) State-conditions on the expected departure time of the bus at the stop
These state-conditions compare the expected departure time from stop
$\tilde{k}_{s}\leq k^\mathrm{d}_{s}$ $\tilde{k}_{s}> k^\mathrm{d}_{s}$ $\tilde{k}_{s} - k^\mathrm{d}_{s} \leq d_{s}$ $s$ $d_{s}$
c) State-conditions on the state of charge of the bus battery
Some conditions concerning the state of charge of the bus battery must be verified as well. These conditions are both related with the minimum level of energy in the battery and with the energy threshold values introduced previously.
Let us start with the conditions that refer to the minimum energy level required to perform the transport service. Specifically, two different state-conditions are defined based on the expected traffic speed: one for the case in which no slowdowns are foreseen (i.e. when condition (V1) is verified) and one for the case in which the average speed on the route is expected to be lower than the one required to meet the bus timetable (i.e. when condition (V2) is verified). This distinction is due to the fact that, in case of congestion, the time taken to reach the subsequent stop, calculated on the basis of the average traffic speed given by (47), is greater than the one required by the timetable causing higher energy consumption. Therefore, the state-conditions to be verified at each stop
\begin{align*} e^\mathrm{min} \leq e_{s}(\tilde{k}_{s})- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r\leq \bar{s}} \biggl [ \Pi _{r}\delta + \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{t}_{r}\beta \biggr ] \\ - \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r< \bar{s}}\Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\beta \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, \rm min}+\Delta ^{e}_{s} \end{align*} View Source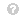 \begin{align*}
e^\mathrm{min} \leq e_{s}(\tilde{k}_{s})- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r\leq \bar{s}} \biggl [ \Pi _{r}\delta + \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{t}_{r}\beta \biggr ] \\
- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r< \bar{s}}\Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\beta \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, \rm min}+\Delta ^{e}_{s}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
e^\mathrm{min} \leq e_{s}(\tilde{k}_{s})- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r\leq \bar{s}} \biggl [ \Pi _{r}\delta + \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{t}_{r}\beta \biggr ] \\
- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r< \bar{s}}\Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\beta \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, \rm min}+\Delta ^{e}_{s}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*} & e^\mathrm{min} \leq e_{s}(\tilde{k}_{s})- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r\leq \bar{s}} \biggl [ \Pi _{r}\delta \\ &\quad + \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot \bigg \lceil \frac{\Pi _{r}}{\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{r}\left(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{r}\right)\Delta _\mathrm{T}}\bigg \rceil \beta \biggr ] \\ &\quad - \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r< \bar{s}} \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\beta \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, \rm min}+\Delta ^{e, \rm c}_{s} \end{align*} View Source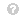 \begin{align*}
& e^\mathrm{min} \leq e_{s}(\tilde{k}_{s})- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r\leq \bar{s}} \biggl [ \Pi _{r}\delta \\
&\quad + \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot \bigg \lceil \frac{\Pi _{r}}{\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{r}\left(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{r}\right)\Delta _\mathrm{T}}\bigg \rceil \beta \biggr ] \\
&\quad - \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r< \bar{s}} \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\beta \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, \rm min}+\Delta ^{e, \rm c}_{s}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
& e^\mathrm{min} \leq e_{s}(\tilde{k}_{s})- \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r\leq \bar{s}} \biggl [ \Pi _{r}\delta \\
&\quad + \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot \bigg \lceil \frac{\Pi _{r}}{\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{r}\left(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{r}\right)\Delta _\mathrm{T}}\bigg \rceil \beta \biggr ] \\
&\quad - \sum _{r\in \mathcal {S}:s< r< \bar{s}} \Delta _\mathrm{T}\cdot T^\mathrm{w}_{r}\beta \leq e^\mathrm{{bus}, \rm min}+\Delta ^{e, \rm c}_{s}
\end{align*}
In (E1) and (E2)
Other state-conditions are relevant to the energy thresholds that must be reached at each stop to achieve the desired final energy level:
$e^\mathrm{{bus}}(\tilde{k}_{s})> \bar{e}_{s}(e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0))$ $e^\mathrm{{bus}}(\tilde{k}_{s})< \bar{e}_{s}(e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0))$ $e^\mathrm{{bus}}(\tilde{k}_{s})= \bar{e}_{s}(e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0))$
Note that the energy threshold values expressed by (48) and used in conditions (E3)–(E5) depend on the initial state of charge of the bus and should be calculated as soon as the bus is ready to start its ride from
B. Control Algorithm
The control algorithm proposed in this paper is run every time the bus is waiting at a stop
Step 0
When the bus is ready to leave stop
$s=0$ $\bar{e}_{s}(e^\mathrm{{bus}}(0))$ $s \in \mathcal {S}$ Step 1
Run the traffic prediction model as described in Section II and obtain the predicted traffic speed
$v^\mathrm{traffic}_{i}(k)$ $i\in \mathcal {I}$ $k \in \mathcal {K}(\tilde{k}_{s})$ Step 2
Compute the average traffic speed
$\bar{v}^\mathrm{traffic}_{s+1}(\tilde{k}_{s}|\tilde{k}_{s}+T^\mathrm{t}_{s+1})$ $s$ $s+1$ Step 3
Identify the current event with the event selector
Step 4
Solve the optimal control problem specific to the event resulting from Step 3, as detailed below, and apply the control actions
$v^\mathrm{{bus}}(k)$ $w^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s+1}(k)$ $c^\mathrm{{bus}}_{s+1}(k)$ $k = \tilde{k}_{s}, \ldots, \tilde{k}_{s+1}$ $s$ $s \ne S$
C. Event Selector
As already mentioned, the decision regarding the optimal control problem to be solved at each bus stop depends on which event is identified as the current one. The procedure for selecting events is illustrated below. Note that these events result from all possible combinations of the state and scenario conditions illustrated above, which, for the sake of simplicity, are grouped into four cases.
The verification of the state-conditions (T1), (T2) and the scenario-conditions (V1), (V2), leads to the following four different cases
Case 1: Conditions (T1) and (V1) are verified (no delay and no slowdowns)
Case 2: Conditions (T1) and (V2) are verified (no delay and slowdowns)
Case 3: Conditions (T2) and (V1) are verified (delay and no slowdowns)
Case 4: Conditions (T2) and (V2) are verified (delay and slowdowns)
The details of Case 1 - Case 4 and their associated sets of events are given hereinafter
1) Case 1
This case gathers all the events that occur when conditions (T1) and (V1) are verified jointly, i.e. when there is no cumulated delay and there are no slowdowns. Then, let us denote with
It occurs when conditions (T1), (V1) and (E1) (and consequently (E4)) are jointly verified. For this event, give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T1), (V1) and (E3) are met. For this event, give priority to
$F_{1}$
It occurs when conditions (T1), (V1) and (E4) are satisfied, but condition (E2) is not verified. For this event, give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T1), (V1) and (E5) are verified. For this event, find the control variables by applying Problems 2-3 (or Problems 5-6) by properly choosing the parameter
$\Delta _{F_{2}}$ $\Delta _{F_{1}}$
Note that, when
2) Case 2
This case collects all the events that take place when conditions (T1) and (V2) are both verified, i.e. the case without cumulated delay and with slowdowns. Therefore, we denote with
It occurs when conditions (T1), (V2) and (E2) (and consequently (E4)) are satisfied. For this event, give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T1), (V2), (V3) and (E4) are simultaneously fulfilled, but condition (E2) is not verified. For this event, give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T1), (V2) and any of conditions (E3)-(E5) are met, but condition (E2) is not verified. For this event, give priority to
$F_{1}$
Note that, if in case
3) Case 3
This case brings together all the events that involve the joint verification of conditions (T2) and (V1), namely when there is cumulated delay and there are no slowdowns. For Case 3, we introduce the set of events
It occurs when conditions (T2), (V1) and (E1) (and consequently (E4)) are satisfied. For this event, give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T2), (V1), (T3) and (E4) are met, but condition (E2) is not verified. For this event, give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T2), (V1), and any of conditions (E3)-(E5) are fulfilled, but condition (E2) is not met. For this event, give priority to
$F_{1}$
If, in case
4) Case 4
This case collects all events that correspond to the simultaneous activation of conditions (T2) and (V2), i.e. when both cumulated delay and slowdowns are present. Thus, let us denote with
It occurs when conditions (T2), (V2), and (E2) (and consequently (E4)) are verified. For this event, give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T2), (V2), (T3), (V3) and (E4) are verified, but condition (E2) is not met. For this event give priority to
$F_{2}$
It occurs when conditions (T2), (V2), and any of conditions (E3)-(E5) are fulfilled, but condition (E2) is not met and conditions (T3), (V3) are not jointly satisfied. For this event, give priority to
$F_{1}$
If in case
D. Simulation Results
In this section, the proposed Pareto-optimal event-based control algorithm has been tested on Ride A described in Section III-B. This ride is performed during the rush hour, for which we considered a 3-minute initial delay and an initial state of charge
The parameters used for checking the state-conditions are given in Table 9. For each
The solutions obtained with the proposed control scheme have been compared with those obtained by solving two single-objective problems, in which only
The comparison has been performed by computing the following indicators:
![]() \begin{align*}
D_{S} =& \Delta _\mathrm{T} \bigl (\tilde{k}^\mathrm{a}_{S} - k^\mathrm{a}_{S}\bigr) \tag{50}\\
\Delta _{SOC} =& SOC(K) - \overline{SOC} \tag{51}
\end{align*}
\begin{align*}
D_{S} =& \Delta _\mathrm{T} \bigl (\tilde{k}^\mathrm{a}_{S} - k^\mathrm{a}_{S}\bigr) \tag{50}\\
\Delta _{SOC} =& SOC(K) - \overline{SOC} \tag{51}
\end{align*}
According to the control algorithm previously introduced, at each stop
As it is shown in Table 10, by starting the ride with a three-minute delay, the control algorithm initially selects the event C3.c and chooses
The results obtained from the application of the proposed control algorithm are shown in Figures 3–5. In particular, Fig. 3 shows the values of the control variables
Dwell time (green line) and charging time (yellow line) compared with reference value
State of charge of the bus during the ride (blue solid line) and desired state of charge (red dashed line).
By applying the event-based control approach proposed in this paper, the state of charge at the terminus is about 51% (approximately 16% less than the desired one), while the cumulated delay at the terminus is 1 minute. Comparing this solution with the solutions obtained with the other methods (Table 11), it can be observed that the proposed controller provides an intermediate solution which better balances the two control objectives. Specifically, analyzing the results of the single-objective problems, it can be stated that the two objectives
Conclusion and Future Works
In this paper station and inter-station control of electric and automated buses in an inter-city road line has been addressed, in order to find the optimal speed profile along the road, and the dwell/charging times at stops. The proposed control scheme is event-based, in that it identifies in real time the occurrence of a specific event, characterized by the joint fulfillment of a set of state and scenario conditions, and decides on the type of multi-objective control method to be applied to the system to find the most suitable solution. Specifically, the proposed control scheme includes two objectives to be optimized: one related to the minimization of the deviation from the bus timetable and the other referring to the final energy level stored in the bus battery. It is important to note that more than two objectives can be considered in the formulation of the optimization problem. However, it should be specified that, as the number of objectives increases, the complexity of the Pareto frontier analysis and the number of optimization problems to be solved in real time to determine the bus control actions increases. The applied methods, based on the lexicographic approach combined with the epsilon-constrained method, guarantee that the solutions found are Pareto-optimal. Different simulation tests based on real data have been presented and discussed in the paper, showing the good performance of the proposed control scheme. This work lays the basis for the definition of a multi-scale control strategy in which the control scheme proposed here represents the high-level control module that will be coupled with a low-level control module that takes into account the effective dynamics of the bus, the real energy consumption and the actual charging performance at the stop. This multi-scale control scheme will be extended in the future to consider the centralized case for controlling bus fleets. In the centralized case, additional constraints will be added to the multi-objective optimization problem to co-ordinate the presence of buses at the stops and to avoid bunching phenomena.
NOTE
Open Access funding provided by ‘Università degli Studi di Genova’ within the CRUI CARE Agreement


















